Search Results for: nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Abiotic Fixation
Definition noun It is part in nitrogen cycle wherein atmospheric nitrogen fixation carries out non-living components to... Read More
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria Definition Cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic bacteria widely distributed in various aquatic habitats... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Diazotroph
Definition noun, plural: diazotrophs A microorganism capable of assimilating and fixing atmospheric nitrogen... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Hatch-Slack pathway
Definition noun A metabolic pathway first delineated in depth by M. D. Hatch and C. R. Slack (in 1966). In this pathway, the... Read More
C4 carbon fixation pathway
Definition noun A metabolic pathway where CO2 is first added to phosphoenolpyruvate by the enzyme, PEP carboxylase,... Read More
Hsk pathway
Definition noun An abbreviation for hatch slack kortshak pathway: a metabolic pathway first determined by Burr and Kortshak... Read More
Bacterioplankton
Definition noun The bacterial component of plankton of aquatic ecosystems Supplement Plankton pertain to the small organisms... Read More
C3 carbon fixation pathway
Definition noun A metabolic pathway where CO2 is converted to 3-phosphogylycerate, the first stable intermediate organic... Read More
Denitrification
The conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas which is then released into the atmosphere. This is caused by bacteria and how... Read More
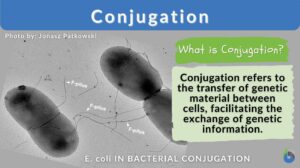
Conjugation
Conjugation generally means the joining or coming together (union), such as in certain unicellular organisms (some bacteria,... Read More
Photolysis
Photolysis Definition We define photolysis as a chemical process in which chemical compounds or molecules are split into... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More